Departmental Results Report (DRR) 2017-2018
Northern Pipeline Agency
2017–18
Departmental Results Report
The Honorable Amarjeet Sohi, P.C. M.P.
Minister of Natural Resources
© Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, as represented by the Minister of Natural Resources, 2018
Cat. No. BT31-2/2018III-31
ISSN 2368-4054
This report is published separately in both official languages.
Copies are available on the Northern Pipeline Agency website
Printed in Canada
Table of contents
Commissioner’s message

It is my pleasure to present the 2017-18 Departmental Results Report for the Northern Pipeline Agency (the Agency).
The Agency was established by the Northern Pipeline Act (the Act) in 1978 to facilitate the planning and construction by Foothills Pipe Lines Limited (Foothills) of the Canadian portion of the Alaska Highway Gas Pipeline (AHGP) project and to maximize social and economic benefits from its construction and operation while minimizing any adverse effects. The pipeline was certificated in 1978 under the Act to transport Alaskan and possibly northern Canadian natural gas to southern markets in Canada and the United States, as provided for by the Canada-U.S. Agreement on Principles Applicable to a Northern Natural Gas Pipeline.
The southern portion of the pipeline was constructed in the early 1980s and presently transports Canadian gas to commercial markets. Unfavourable economic conditions have led to several delays in the completion of the northern portion of the pipeline.
In 2008, TransCanada PipeLines Limited (TransCanada), which now owns Foothills, was selected by the State of Alaska to pursue a large-scale pipeline project that would transport natural gas in a large diameter buried pipeline from Prudhoe Bay, Alaska to Boundary Lake, Alberta using the northern portion of the AHGP project. However, TransCanada notified the Agency in February 2013 that no further work is planned on the AHGP for now and will await further commercial interest before recommencing its efforts.
To align with the reduction in the AHGP project activities for the foreseeable future, the Agency has scaled down its operations to a minimal level while continuing to fulfill Canada’s ongoing obligations as set out in the Act. During this time, the Agency will also respond to any incoming inquiries from other government agencies, Indigenous groups and the public.
Christyne Tremblay
Commissioner
Results at a glance
For more information on the Agency’s plans, priorities and results achieved, see the “Results: what we achieved” section of this report.
- What funds were used? $5,541,166
- Who was involved? 1 Full-Time Equivalent (FTE)
- Results Highlights
- The Northern Pipeline Agency has scaled down its operations to a minimal level to fulfill Canada’s ongoing obligations as set out in the Northern Pipeline Act.
- The Agency exceeded its target for performance in responding to requests from external parties in a timely fashion.
Raison d’être, mandate and role: who we are and what we do
Raison d’être
The Northern Pipeline Agency (Agency) was established by the Northern Pipeline Act in 1978 and, in the context of the 1977 Agreement between Canada and the United States of America on Principles Applicable to a Northern Natural Gas Pipeline. The Agency has a mandate to carry out federal responsibilities in respect of the planning and construction of the Canadian portion of the Alaska Natural Gas Pipeline. The Agency plays a key role in supporting efficient and expeditious regulatory approval while ensuring environmental protection and social and economic benefits for Canada.
Mandate and role
The Agency was created under the Act in 1978 to:
- facilitate the efficient and expeditious planning and construction of the Canadian portion of the Alaska Highway Gas Pipeline (AHGP) project, taking into account local and regional interests, the interests of the residents, particularly of Indigenous Peoples, and recognizing the responsibilities of the Government of Canada and other governments, as appropriate;
- facilitate, in relation to the pipeline, consultation and coordination with the governments of the provinces, the Yukon Territory, and the Northwest Territories;
- maximize the social and economic benefits from the construction and operation of the pipeline while at the same time minimizing any adverse effect on the social and environmental conditions of the areas most directly affected by the pipeline; and
- advance national economic and energy interests and maximize related industrial benefits.
For more general information about the Agency, see the “Supplementary information” section of this report. For more information on the Minister of Natural Resources’ mandate letter commitments, see the Minister's mandate letter.
Operating context and key risks
Operating context
The Agency was responsible for the regulatory oversight of the construction of Phase I (the southern portion) of the AHGP (also known as the Prebuild) in 1981-82 for the initial purpose of transporting gas sourced from Western Canada to the United States (U.S.). These facilities, located in southern British Columbia, Alberta and Saskatchewan, were expanded five times between 1985 and 1998 under the authority of the Act. The current flow capacity of the Prebuild is approximately 94.5 million cubic metres per day (3.3 billion cubic feet per day).
Phase II (the northern portion) of the AHGP would link the Prebuild with U.S. natural gas reserves at Prudhoe Bay in Alaska. Economic conditions since 1982 have led to several delays in the completion of the AHGP and fluctuating activity levels for the Agency. Prior to commencing construction of this section of the pipeline, Foothills/TransCanada is required to obtain a comprehensive series of specific approvals from the Agency as set out under the Act. These approvals relate to socio-economic and environmental requirements, routing, technical and engineering design and other matters, such as the demonstration of project financing.
The Agency is also responsible for the administration of the Canada - Foothills easement agreement, which was entered into on November 24, 1983. Pursuant to the decision under the Act, a grant of easement was issued by Order in Council on November 28, 1983. The easement follows the Alaska Highway from the Yukon-Alaska border near Beaver Creek, Yukon, to the Yukon-British Columbia border near Watson Lake, Yukon. The easement agreement allows Foothills/TransCanada to conduct investigative work on easement lands; however, the company requires the approval of the minister responsible for the Agency before it can begin pipeline construction. Unless the term is once again amended, the agreement will expire on September 20, 2022. In addition to the easement, the Agency holds approximately 220 reserves of land along the pipeline route that could be used to support the construction and operation of the pipeline system.
To align with the reduction in the AHGP project activities for the foreseeable future, the Agency has scaled down its operations to a minimal level to fulfill Canada’s ongoing obligations as set out in the Act. During this time of reduced activities, the Agency will also respond to any incoming inquiries from other government agencies, Indigenous groups and the public. The future of the northern portion of the AHGP continues to rest with its proponents and the commercial marketplace.
Key risks
In May 2012, Foothills/TransCanada notified the Agency that no regulatory filings were planned on the AHGP for now and of their intentions to maintain the AHGP project assets in Canada. Foothills/TransCanada informed the Agency in February 2013 that no further work is planned on the AHGP and that it will await further commercial interest before recommencing its efforts.
The challenge before the Agency is to preserve the progress and outcomes achieved in recent years to deliver an efficient and effective regulatory review framework of updated environmental, socio-economic and technical information which takes into account changes since the Act came into force and the pipeline was certificated in the late 1970s. Failure to be positioned for timely preparations, should the project be resumed, could jeopardize the Government of Canada’s performance of its responsibilities under the Act.
| Risks | Mitigating strategy and effectiveness | Link to the department’s Programs | Link to mandate letter commitments or to government‑wide and departmental priorities |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Agency needs to be able to manage its ongoing core responsibilities and be in a position to adjust quickly should the proponent receive a clear positive response from the marketplace, and Phase II work is resumed. | The Agency will continue to maintain a minimum level of resources to fulfil ongoing responsibilities until such time as Foothills/TransCanada resumes the project, or that Agency actions or federal decisions are needed. | Oversee and regulate the planning and construction of the Canadian portion of the Alaska Highway Gas Pipeline Project. | Not applicable |
Results: what we achieved
Programs
Program name
Oversee and regulate the planning and construction of the Canadian portion of the Alaska Highway Natural Gas Pipeline Project.
Description
Oversee and regulate the planning and construction of the Canadian portion of the Alaska Highway Natural Gas Pipeline Project.
Results
| Expected results | Performance indicators | Target | Date to achieve target | 2017–18 Actual results |
2016–17 Actual results |
2015–16 Actual results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Agency will maintain the appropriate minimum level of preparation activities for a regulatory framework, so as to remain prepared to ramp up quickly to effectively regulate and facilitate the planning and construction of the pipeline should the project proceed. | The Agency will respond to company and public correspondence within 15 business days of receipt. | 80% | Annual basis | 100% | 100% | 100% |
In 2017-2018, the Agency received only one request from the public.
| 2017–18 Main Estimates |
2017–18 Planned spending |
2017–18 Total authorities available for use |
2017–18 Actual spending (authorities used) |
2017–18 Difference (actual minus planned) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 494,830 | 494,830 | 5,784,361 | 5,541,166 | 5,046,336 |
The increase between Planned spending and Actual spending is mainly attributed to a remittance to TransCanada representing the outstanding over-collection balance of $5,315,360 from Foothills that had accumulated as of December 14, 2017. This over-collection balance occurred as a result of the Agency’s cost-recovery mechanism, based on forecasted expenditures. The Northern Pipeline Act was amended on December 14, 2017 and the cost-recovery mechanism was adjusted to allow the Agency to annually collect an amount equivalent to its actual expenses from Foothills. Authority was subsequently provided to remit the over-collection to the proponent. The overall difference between Planned and Actual spending was slightly offset by reduced spending in program expenditures, which aligns with the reduction in the AHGP project activities.
| 2017–18 Planned full-time equivalents |
2017–18 Actual full-time equivalents |
2017–18 Difference (Actual full-time equivalents minus Planned full-time equivalents) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 1 | (3) |
The decrease between Planned FTEs and Actual FTEs is mainly attributed to continued reduction in the AHGP project activities.
The Agency does not have any lower-level programs.
Internal Services
Description
Internal Services are those groups of related activities and resources that the federal government considers to be services in support of programs and/or required to meet corporate obligations of an organization. Internal Services refers to the activities and resources of the 10 distinct service categories that support program delivery in the organization, regardless of the Internal Services delivery model in a department. The 10 service categories are: Management and Oversight Services; Communications Services; Legal Services; Human Resources Management Services; Financial Management Services; Information Management Services; Information Technology Services; Real Property Services; Materiel Services; and Acquisition Services.
Results
| 2017–18 Main Estimates |
2017–18 Planned spending |
2017–18 Total authorities available for use |
2017–18 Actual spending (authorities used) |
2017–18 Difference (actual minus planned) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
The Agency has a single strategic outcome and a single program. As a small and separate federal entity, the Agency has a service agreement with Natural Resources Canada and expenditures for internal services through this agreement are recorded as program spending.
| 2017–18 Planned full-time equivalents |
2017–18 Actual full-time equivalents |
2017–18 Difference (Actual full-time equivalents minus Planned full-time equivalents) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
Analysis of trends in spending and human resources
Actual expenditures
Departmental spending trend graph
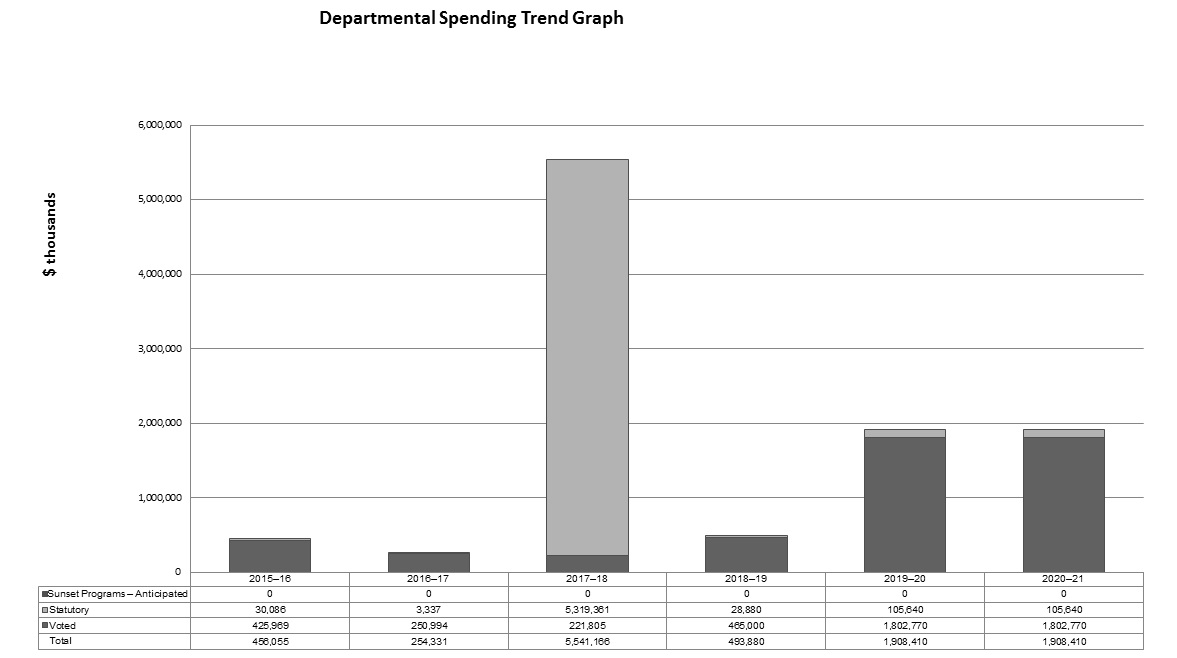
Text version
This bar graph shows the Northern Pipeline Agency planned and actual spending for the fiscal years between 2015-16 and 2020-21.
Total spending and planned spending by period is as follows:
| 2015-16 | 2016-17 | 2017-18 | 2018-19 | 2019-20 | 2020-21 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunset Programs - Anticipated | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Statutory | 30,906 | 3,337 | 5,319,361 | 28,880 | 105,640 | 105,640 |
| Voted | 425,969 | 250,994 | 221,805 | 465,000 | 1,802,770 | 1,802,770 |
| Total | 456,055 | 254,331 | 5,541,166 | 493,880 | 1,908,410 | 1,908,410 |
The Agency’s Voted actual spending has decreased each year between 2015-16 and 2017-18. This reduction in spending aligns with the reduction in the AHGP project activities while continuing to fulfill Canada’s obligations under the Act. The actual Statutory spending increased in 2017-18 due to a remittance to TransCanada representing the outstanding over-collection balance from Foothills that had accumulated as of December 14, 2017. This over-collection balance occurred as a result of the Agency’s cost-recovery mechanism, based on forecasted expenditures. The Northern Pipeline Act was amended on December 14, 2017 and the cost-recovery mechanism was adjusted to allow the Agency to annually collect an amount equivalent to its actual expenses from Foothills. Authority was subsequently provided to remit the over-collection to the proponent. The Agency’s forecasted spending for 2018-19 onwards reflects the increased funding allocated to the Agency when Phase II (the northern portion) of the project was being advanced by Foothills/TransCanada. The planned spending in 2019-20 and future years will be re-assessed in 2018-19 and adjusted as necessary.
| Programs and Internal Services | 2017–18 Main Estimates |
2017–18 Planned spending |
2018–19 Planned spending |
2019–20 Planned spending |
2017–18 Total authorities available for use |
2017–18 Actual spending (authorities used) |
2016–17 Actual spending (authorities used) |
2015–16 Actual spending (authorities used) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oversee and regulate the planning and construction of the Canadian portion of the AHGP Project. | 494,830 | 494,830 | 493,880 | 1,908,410 | 5,784,361 | 5,541,166 | 254,331 | 456,055 |
| Subtotal | 494,830 | 494,830 | 493,880 | 1,908,410 | 5,784,361 | 5,541,166 | 254,331 | 456,055 |
| Internal Services | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 494,830 | 494,830 | 493,880 | 1,908,410 | 5,784,361 | 5,541,166 | 254,331 | 456,055 |
In 2017-18, the Agency spent $5,541,166 compared to the planned spending of $494,830. The increase is mainly attributed to a one-time remittance to TransCanada representing the outstanding over-collection balance of $5,315,360 from Foothills that had accumulated as of December 14, 2017, which was slightly offset by ongoing reduced program spending. The reduction in spending since 2015-16 aligns with the reduction in the AHGP project activities, while the Agency continues to fulfill Canada's obligations under the Act.
Actual human resources
| Programs and Internal Services | 2015–16 Actual full-time equivalents |
2016–17 Actual full-time equivalents |
2017–18 Planned full-time equivalents |
2017–18 Actual full-time equivalents |
2018–19 Planned full-time equivalents |
2019–20 Planned full-time equivalents |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oversee and regulate the planning and construction of the Canadian portion of the Alaska Highway Natural Gas Pipeline Project. | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Subtotal | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Internal Services | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
Expenditures by vote
For information on the Agency’s organizational voted and statutory expenditures, consult the Public Accounts of Canada 2018.
Government of Canada spending and activities
Information on the alignments of the NPA’s spending with the Government of Canada’s spending and activities is available in the GC InfoBase.
Financial statements and financial statements highlights
Financial statements
The Agency’s financial statements [unaudited] for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2018, are available on the Agency’s website.
Financial statements highlights
The highlights presented in this section are drawn from the Agency’s financial statements.
The financial statements were prepared using the Government of Canada accounting policies, which are based on Canadian public sector accounting standards resulting in figures that may differ from those provided in other sections of the Departmental Results Report prepared on an expenditure basis. A reconciliation between authorities used on an expenditure basis and the net cost of operations prepared on an accrual basis is set out in Note 3 of the Agency’s financial statements.
| Financial Information | 2017–18 PlannedFootnote * |
2017–18 Actual |
2016–17 Actual |
Difference (2017–18 Actual minus 2017–18 Planned) |
Difference (2017–18 Actual minus 2016–17 Actual) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total expenses | 499,693 | 231,582 | 258,873 | (268,111) | (27,291) |
| Total net revenues | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Net cost of operations before government funding and transfers | 499,693 | 231,582 | 258,873 | (268,111) | (27,291) |
Total Agency expenses of $231,582 are consistent with the prior year and the alignment to the reduction in the AHGP project activities while continuing to fulfill Canada’s obligations under the Act.
| Financial Information | 2017–18 | 2016–17 | Difference (2017–18 minus 2016–17) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total net liabilities | 136,825 | 9,277 | 127,548 |
| Total net financial assets | 129,042 | (1,169) | 130,211 |
| Departmental net debt | 7,783 | 10,446 | (2,663) |
| Total non-financial assets | 7,783 | 10,446 | (2,663) |
| Departmental net financial position | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Total Agency net liabilities include accounts payable of $136,825 to other government departments and agencies and an account payable of $5,315,349 to TransCanada related to the remission of the outstanding over-collection balance from Foothills that had accumulated as of December 14, 2017. This over-collection balance occurred as a result of the Agency’s cost-recovery mechanism, based on forecasted expenditures. The Northern Pipeline Act was amended on December 14, 2017 and the cost-recovery mechanism was adjusted to allow the Agency to annually collect an amount equivalent to its actual expenses from Foothills. Authority was subsequently provided to remit the over-collection to the proponent. This amount is also recorded as accounts payable held on behalf of the Government for a nil effect on net liabilities. The increase of $127,548 in accounts payable to other government departments and agencies from 2016-17 is mainly due to late billing.
Total Agency net financial assets of $129,042 consist of $25,829 in accounts receivable from other government departments and agencies and $103,213 in the due from the consolidated revenue fund, which represents amounts that may be disbursed without further charges to the Agency authorities.
Total Agency non-financial assets of $7,783 consist of tangible capital assets. The decrease of $2,663 from 2016-17 is due to the amortization of capital assets.
Supplementary information
Corporate information
Organizational profile
Appropriate minister: The Honourable Amarjeet Sohi, P.C., M.P.
Institutional head: Christyne Tremblay
Ministerial portfolio: Natural Resources
Enabling instrument: Northern Pipeline Act
Year of incorporation / commencement: 1978
Other: The operating costs of the Northern Pipeline Agency to carry out federal responsibilities for the planning and construction of the Alaska Highway Natural Gas Pipeline project are fully recovered from the project proponent, Foothills Pipe Lines Limited. Foothills is now fully owned by TransCanada PipeLines Limited.
Reporting framework
The Agency’s Strategic Outcome and Program Alignment Architecture of record for 2017–18 are shown below.
- 1. Strategic Outcome: The planning and construction of the Canadian portion of the Alaska Highway Gas Pipeline project is efficient and expeditious while ensuring environmental protection and social and economic benefits for Canadians.
- 1.1 Program: Oversee and regulate the planning and construction of the Canadian portion of the Alaska Highway Natural Gas Pipeline Project.
Internal Services
- 1.1 Program: Oversee and regulate the planning and construction of the Canadian portion of the Alaska Highway Natural Gas Pipeline Project.
Supporting information on lower-level programs
The Agency has no lower‑level programs.
Supplementary information tables
The following supplementary information table is available on the Agency’s website:
- User fees, regulatory charges and external fees.
Federal tax expenditures
The tax system can be used to achieve public policy objectives through the application of special measures such as low tax rates, exemptions, deductions, deferrals and credits. The Department of Finance Canada publishes cost estimates and projections for these measures each year in the Report on Federal Tax Expenditures. This report also provides detailed background information on tax expenditures, including descriptions, objectives, historical information and references to related federal spending programs. The tax measures presented in this report are the responsibility of the Minister of Finance.
Organizational contact information
The Northern Pipeline Agency has been designated as a department for the purposes of the Financial Administration Act. The Agency currently reports to Parliament through the Minister of Natural Resources, who is responsible for the management and direction of the Agency. The Agency has one senior officer, a Commissioner appointed by the Governor in Council. The Commissioner is currently the Deputy Minister of Natural Resources Canada. The Northern Pipeline Agency’s organizational structure is defined by the Northern Pipeline Act.
The Agency’s contact information is as follows:
Mailing address:
470-588 Booth Street
Ottawa, ON K1A 0Y7
Phone: (613) 995-1150
Email: info@npa-apn.gc.ca
Appendix: definitions
- appropriation (crédit)
- Any authority of Parliament to pay money out of the Consolidated Revenue Fund.
- budgetary expenditures (dépenses budgétaires)
- Operating and capital expenditures; transfer payments to other levels of government, organizations or individuals; and payments to Crown corporations.
- Departmental Plan (Plan ministériel)
- A report on the plans and expected performance of an appropriated department over a three‑year period. Departmental Plans are tabled in Parliament each spring.
- Departmental Results Report (Rapport sur les résultats ministériels)
- A report on the appropriated department’s actual accomplishments against the plans, priorities and expected results set out in the corresponding Departmental Plan.
- Evaluation (évaluation)
- In the Government of Canada, the systematic and neutral collection and analysis of evidence to judge merit, worth or value. Evaluation informs decision making, improvements, innovation and accountability. Evaluations typically focus on programs, policies and priorities and examine questions related to relevance, effectiveness and efficiency. Depending on user needs, however, evaluations can also examine other units, themes and issues, including alternatives to existing interventions. Evaluations generally employ social science research methods.
- experimentation (expérimentation)
- Activities that seek to explore, test and compare the effects and impacts of policies, interventions and approaches, to inform evidence-based decision-making, by learning what works and what does not.
- full‑time equivalent (équivalent temps plein)
- A measure of the extent to which an employee represents a full person‑year charge against a departmental budget. Full‑time equivalents are calculated as a ratio of assigned hours of work to scheduled hours of work. Scheduled hours of work are set out in collective agreements.
- gender-based analysis plus (GBA+) (analyse comparative entre les sexes plus [ACS+])
- An analytical approach used to assess how diverse groups of women, men and gender-diverse people may experience policies, programs and initiatives. The “plus” in GBA+ acknowledges that the gender-based analysis goes beyond biological (sex) and socio-cultural (gender) differences. We all have multiple identity factors that intersect to make us who we are; GBA+ considers many other identity factors, such as race, ethnicity, religion, age, and mental or physical disability. Examples of GBA+ processes include using data disaggregated by sex, gender and other intersecting identity factors in performance analysis, and identifying any impacts of the program on diverse groups of people, with a view to adjusting these initiatives to make them more inclusive.
- government-wide priorities (priorités pangouvernementales)
- For the purpose of the 2017–18 Departmental Results Report, those high-level themes outlining the government’s agenda in the 2015 Speech from the Throne, namely: Growth for the Middle Class; Open and Transparent Government; A Clean Environment and a Strong Economy; Diversity is Canada's Strength; and Security and Opportunity.
- horizontal initiatives (initiative horizontale)
- An initiative where two or more departments are given funding to pursue a shared outcome, often linked to a government priority.
- Management, Resources and Results Structure (Structure de la gestion, des ressources et des résultats)
- A comprehensive framework that consists of an organization’s inventory of programs, resources, results, performance indicators and governance information. Programs and results are depicted in their hierarchical relationship to each other and to the Strategic Outcome(s) to which they contribute. The Management, Resources and Results Structure is developed from the Program Alignment Architecture.
- non‑budgetary expenditures (dépenses non budgétaires)
- Net outlays and receipts related to loans, investments and advances, which change the composition of the financial assets of the Government of Canada.
- performance (rendement)
- What an organization did with its resources to achieve its results, how well those results compare to what the organization intended to achieve, and how well lessons learned have been identified.
- performance indicator (indicateur de rendement)
- A qualitative or quantitative means of measuring an output or outcome, with the intention of gauging the performance of an organization, program, policy or initiative respecting expected results.
- performance reporting (production de rapports sur le rendement)
- The process of communicating evidence‑based performance information. Performance reporting supports decision making, accountability and transparency.
- plan (plan)
- The articulation of strategic choices, which provides information on how an organization intends to achieve its priorities and associated results. Generally a plan will explain the logic behind the strategies chosen and tend to focus on actions that lead up to the expected result.
- planned spending (dépenses prévues)
-
For Departmental Plans and Departmental Results Reports, planned spending refers to those amounts that receive Treasury Board approval by February 1. Therefore, planned spending may include amounts incremental to planned expenditures presented in the Main Estimates.
A department is expected to be aware of the authorities that it has sought and received. The determination of planned spending is a departmental responsibility, and departments must be able to defend the expenditure and accrual numbers presented in their Departmental Plans and Departmental Results Reports.
- priority (priorité)
- Plans or projects that an organization has chosen to focus and report on during the planning period. Priorities represent the things that are most important or what must be done first to support the achievement of the desired Strategic Outcome(s).
- program (programme)
- A group of related resource inputs and activities that are managed to meet specific needs and to achieve intended results and that are treated as a budgetary unit.
- Program Alignment Architecture (architecture d’alignement des programmes)
- A structured inventory of an organization’s programs depicting the hierarchical relationship between programs and the Strategic Outcome(s) to which they contribute.
- result (résultat)
- An external consequence attributed, in part, to an organization, policy, program or initiative. Results are not within the control of a single organization, policy, program or initiative; instead they are within the area of the organization’s influence.
- statutory expenditures (dépenses législatives)
- Expenditures that Parliament has approved through legislation other than appropriation acts. The legislation sets out the purpose of the expenditures and the terms and conditions under which they may be made.
- Strategic Outcome (résultat stratégique)
- A long‑term and enduring benefit to Canadians that is linked to the organization’s mandate, vision and core functions.
- sunset program (programme temporisé)
- A time‑limited program that does not have an ongoing funding and policy authority. When the program is set to expire, a decision must be made whether to continue the program. In the case of a renewal, the decision specifies the scope, funding level and duration.
- target (cible)
- A measurable performance or success level that an organization, program or initiative plans to achieve within a specified time period. Targets can be either quantitative or qualitative.
- voted expenditures (dépenses votées)
- Expenditures that Parliament approves annually through an Appropriation Act. The Vote wording becomes the governing conditions under which these expenditures may be made.
Page details
- Date modified: